Overview of Iodine metabolism.
- Diet –> absorbed from GIT into circulation–> 500mcg/L
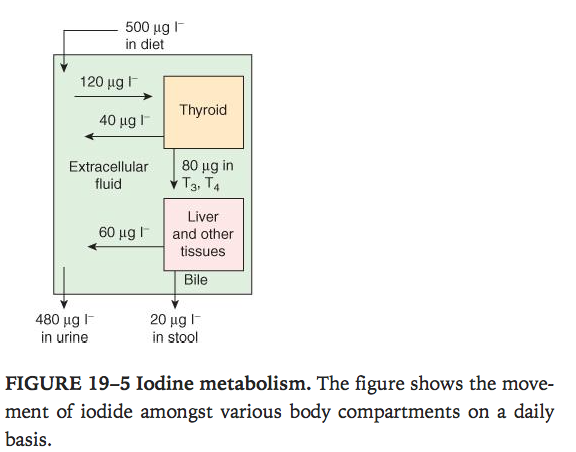
Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 24th Edition
T3 / T4 synthesis / secretion.
- More amount of T4 secreted than T3 but T3 is more biologically active.
- T3 is made at site of action by deiodinating T4.
- Reverse T3 is not biologically active
- At interface between thyrocyte and colloid, iodide undergoes organification.
- Iodide –> iodine
- Incorporated into carbon 3 of thyroglobulin molecule in colloid (thyroid peroxidase on thyrocyte apical membrane)
- The thyroid hormone sythesised remains in colloid and when required the thyrocytes endocytose part of the colloid–> lysosomal degradation–> free T4 and T3 released into circulation
- TPO generates reactive iodine species which react with thyroglobulin–> first product is MIT monoiodotyrosine
- MIT is then iodinated at carbon 5 –> di-iodotyrosine(DIT) (by iodotyrosine deiodinase)
- DIT +DIT = T4 + alanine
- MIT + DIT = T3 + alanine
Effects of T3 / T4.
- T3 bind to receptor in nucleus (T4 binds less avidly) –> T3/receptor complex binds DNA –> transcription of cell proteins to effect functions.
- Stimulate O2 consumption
- Control level of metabolism
- Help regulate lipid and carbohydrate metabolism
- Influence body mass and Mentation
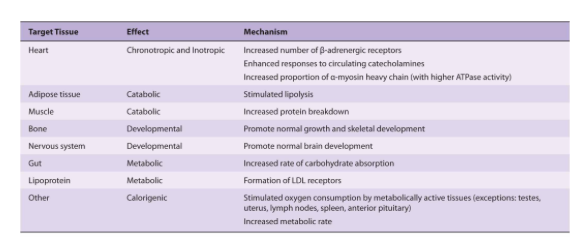
Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 24th Edition
Regulation of T3 / T4 secretion.
- Throtrophin releasing hormone from hypothalamus
- Thyroid stimulating hormone from anterior pituitary
- T3 and T4 from thyroid which negatively feeds back to the other 2.
Hypothyroidism
- In neonatal or fetal period –> mental retardation, inhibition of growth
- Weight gain
- Slowing of mentation
- Slowing of metabolism
- Cold intolerance
- Hair coarsening
Hyperthyroidism
- Tremor
- Hyper-reflexia
- Increased appetite
- Weight loss
- Heat intollerance
- Agitation, nervousness
- tachycardia
Overview of Ca2+ metabolism
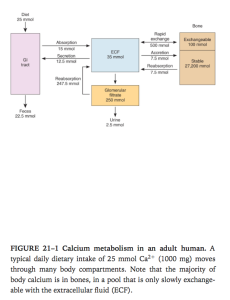
Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 24th Edition
- Young adult has 1100g of Ca
- 99% in skeleton
- Plasma ca is partly bound to protein
- Free ionized calcium in bodily fluids is the key second messenger
- Needed in nerve function, muscle contraction and blood coagulation
Overview of bone physiology.
- A readily exchangeable pool of 100mmol in bone
- Stable pool of 27200mmol –> slower to mobilise
- Osteoclasts break down bone
- Osteoblasts lay down new osteo matrix which gets calcified.
Vitamin D and OH-Cholecalciferols.
- Increases gut absorption of calcium
- Increase renal reabsorption of Ca
- Increases activation of osteoblasts (Vit D needed for normal bone ossification) –> secondary increased activity of osteoclasts.
- 7 dehydrocholesterol –> Vit D3 in skin under UV light(vit D3 also ingested) –> 25 hydroxycholecalciferol (in liver by p450) –> 1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol in kidney (by 1alpha hydroxylase)= calcitriol
- High plasma PO4 inhibits Vit D by inhibiting 1alpha hydroxylase
PTH.
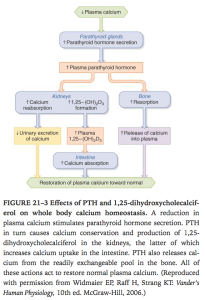
Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 24th Edition
- Actions.
- Increase 1alpha hydroxylase –> increase vit D
- Increase phosphate excretion in kidney
- Stimulate osteoblasts and osteoclasts
- The increased renal Calcium reabsorption maybe offset by the increase in filtered calcium
- Regulation of secretion.
- Low plasma ionised Ca –> increased PTH release
- Negative feedback via Ca binds G protein receptor –> phosphoinositide turnover–> inhibit PTH release
- 1,25dihydroxycholecalciferol acts on parathyroid to decrease preproPTH mRNA
- Increased palsma phosphate lowers plasma free Ca–> increased PTH release
- Mg required for normal PTH secretion
- Made as preproPTH and cleaved before secretion into plasma
Calcitonin.
- Made by the parafollicular cells/clear cells of thyroid
- T 1/2 10mins
- Actions.
- Inhibits osteoclasts –> decrease bone resorption –> Lower plasma calcium
- Increases calcium excretion in urine
- Regulation of secretion.
- Secreted when plasma Ca is high
- Secretion starts when Ca is 9.5mg/dL
- Stimulants
- Beta-adrenergic agonists, dopamine, oestrogens, Gastrin, cholecystokinin, glucagon, and secretin
- gastrin being the most potent stimulus
- plasma calcitonin level is elevated in Zollinger–Ellison syndrome and in pernicious anemia
Viva questions:
- Tell me about the thyroid gland and thyroid hormones.
- Tell me about the metabolism of calcium.
- Tell me about Vitamin D and its role in calcium metabolism



